
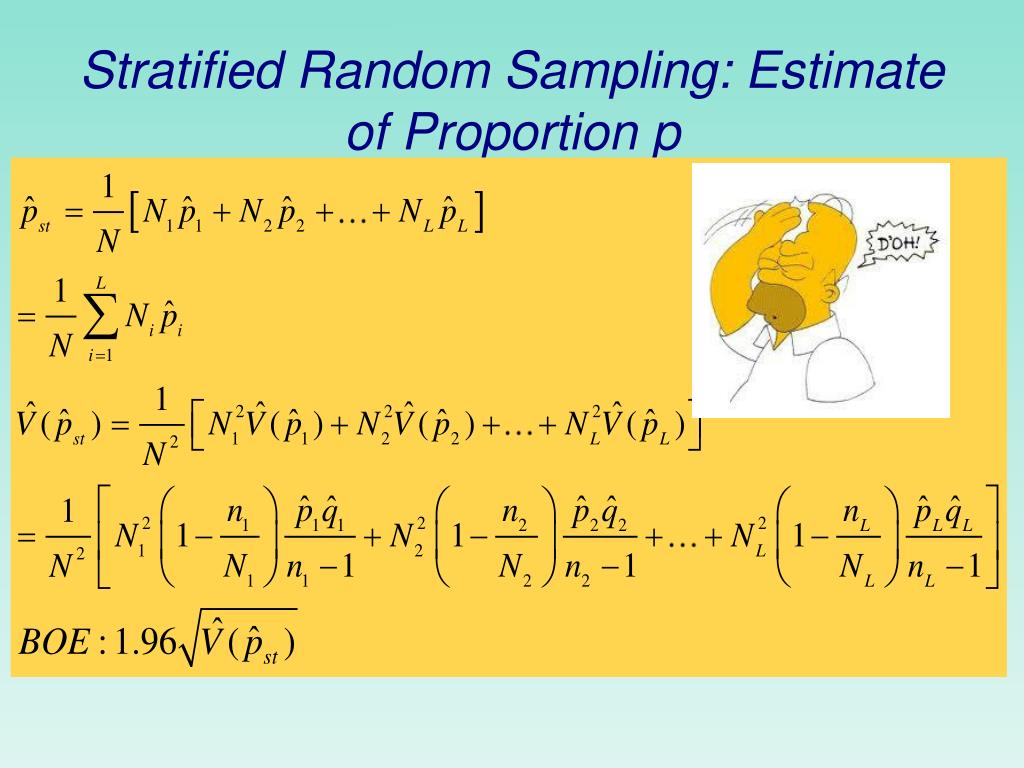
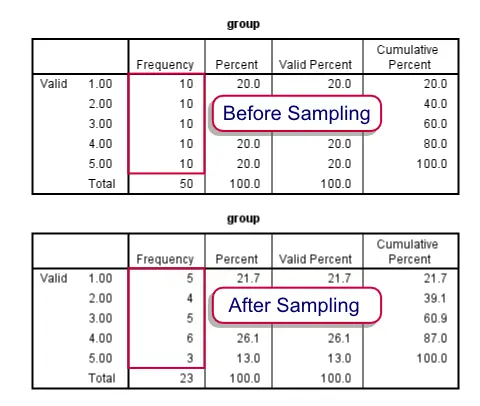
The sample we selected is exactly proportional to the population with regards to teaching level. The sample size for each strata (layer) is proportional to the size of the layer: Sample size of the strata size of. We do the same for the high school teachers and select 60. To get the stratified random sample, you would randomly sample the categories so that your eventual sample size has 39 percent of participants taken from category 1, 38 percent from category 2 and 23 percent from category 3. Similarly, we use a list of all of the middle school teachers and randomly select 40 (20% of 200). Stratified sampling is when the population is divided into specific groups and then randomly sampled from those groups. To achieve this, we obtain a list of all of the elementary teachers in the system. Since 50% of those teachers need to be elementary teachers, we need 100 elementary teachers in our sample (200 X. Stratified sampling is a method of obtaining a representative sample from a population that researchers have divided into relatively similar subpopulations (strata). Stratified sampling lowers the chances of researcher bias and sampling bias, significantly. It is a smart way to ensure that all the sub-groups in your research population are well-represented in the sample. Let’s also assume that we want to sample 200 teachers. Stratified sampling helps you to save cost and time because you’d be working with a small and precise sample. Because those percentages exist in our population, we want our sample to have the same percentages. For this example, we will use 50%, 20% and 30% respectively. It is important to note that the strata must be non-overlapping. The selected unit is then replaced, and these two. Stratified sampling is a probability sampling technique wherein the researcher divides the entire population into different subgroups or strata, then randomly selects the final subjects proportionally from the different strata. In the first draw, a sampling unit is selected with probability pk xk/t(x) p k x k / t ( x), with xk x k the size variable for unit k k and t(x) N k1xk t ( x) k 1 N x k the population total of the size variable. Assume we want the teaching level (elementary, middle school, and high school) in our sample to be proportional to what exists in the population of Hartford teachers.įirst we must determine what percentage of the teachers in the Hartford system are elementary, middle school, and high school. 8.1 Probability-proportional-to-size sampling with replacement. Suppose we wish to study computer use of educators in the Hartford system. STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING – A representative number of subjects from various subgroups is randomly selected.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
